The Gouy balance magnetometer measures magnetic susceptibility in materials, providing insights into their magnetic behavior and properties.
Gouy Balance Magnetometer: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
The Gouy balance magnetometer is a scientific instrument that has garnered significant attention in the field of magnetism and material science. It is employed to determine the magnetic susceptibility of materials, which is a key parameter in understanding the magnetic behavior of various substances. This article delves into the history, working principle, and applications of the Gouy balance magnetometer, offering an in-depth understanding of its significance in research and industry.
History
The Gouy balance magnetometer was invented by French physicist Louis Georges Gouy in 1889 as a method to measure magnetic susceptibilities of materials. Gouy’s ingenious design has since been refined and improved over the years, with modern versions of the instrument now boasting advanced features and enhanced accuracy. Despite the development of alternative techniques, the Gouy balance magnetometer remains a reliable and widely used instrument in magnetism research.
Working Principle
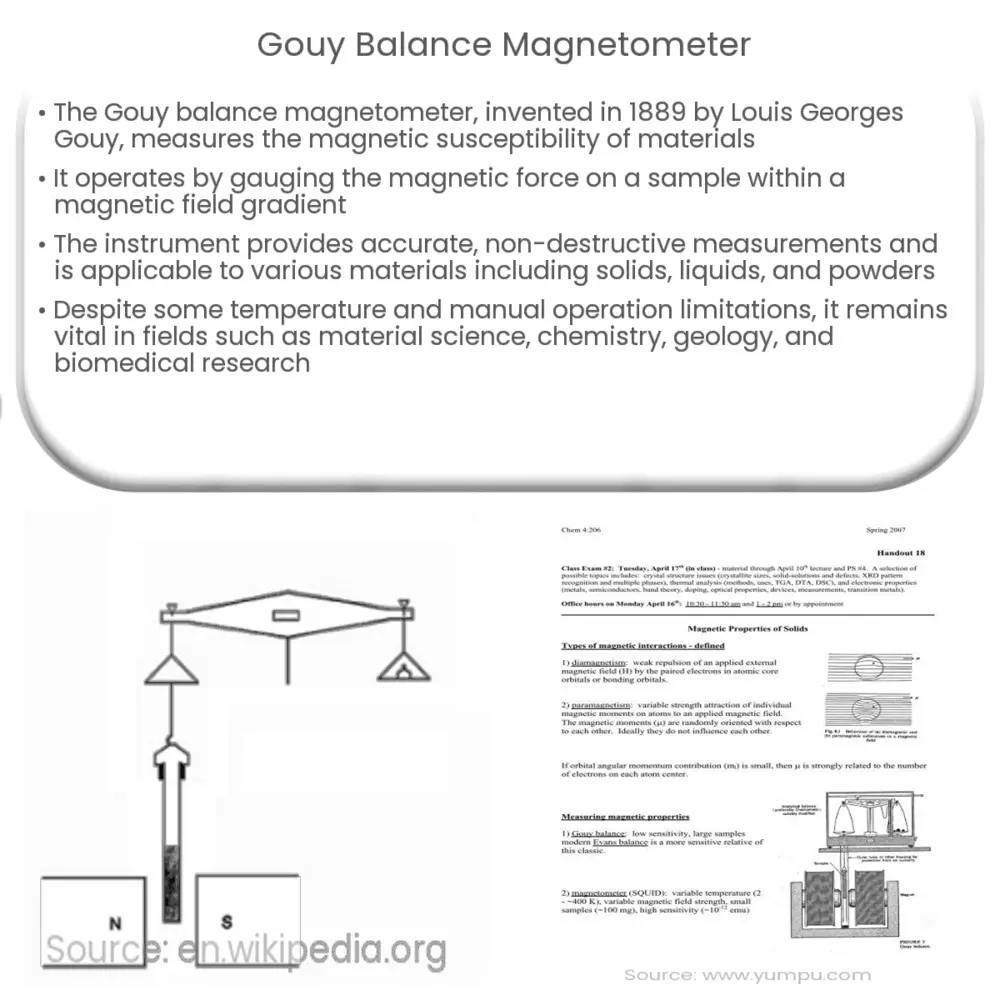
The Gouy balance magnetometer operates on the principle of magnetic force acting on a sample when placed within a magnetic field gradient. The apparatus consists of a sensitive analytical balance, a strong electromagnet with tapered pole pieces, and a non-magnetic sample holder. The magnetic field gradient is produced by the tapered pole pieces, which create a region of non-uniform magnetic field intensity.
When a sample is placed in the magnetic field gradient, it experiences a magnetic force proportional to its magnetic susceptibility and the magnetic field gradient. This force causes the sample to be either attracted or repelled from the region of highest magnetic field intensity, depending on its magnetic properties. The change in weight observed on the balance as a result of this magnetic force is used to calculate the magnetic susceptibility of the sample.
Procedure
A typical Gouy balance magnetometer measurement involves the following steps:
- Calibration: The analytical balance is calibrated to ensure accurate weight measurements.
- Sample preparation: The material to be analyzed is prepared in a suitable form, often as a fine powder or thin film, and placed in the non-magnetic sample holder.
- Weight measurement: The sample holder with the material is weighed in the absence of a magnetic field, providing the initial weight (W0).
- Magnetic field application: The sample holder is positioned within the magnetic field gradient, and the change in weight (ΔW) due to the magnetic force is recorded.
- Magnetic susceptibility calculation: Using the recorded weight change and the known properties of the magnetic field, the magnetic susceptibility of the material can be calculated.
Advantages and Limitations
The Gouy balance magnetometer offers several advantages, making it a popular choice for measuring magnetic susceptibility:
- Applicability to various materials: The technique can be used for a wide range of materials, including solids, liquids, and powders.
- Accuracy and sensitivity: With proper calibration and setup, Gouy balance magnetometers can provide accurate and sensitive measurements of magnetic susceptibility.
- Non-destructive testing: The method does not cause any damage to the sample during the measurement process.
However, there are some limitations to consider:
- Limited temperature range: The technique may not be suitable for materials that exhibit significant changes in magnetic properties at elevated temperatures, as most Gouy balance magnetometers are designed for operation at room temperature.
- Manual operation: The Gouy balance magnetometer requires manual intervention for sample handling and weight measurements, which may introduce errors and limit throughput.
Applications
The Gouy balance magnetometer has found various applications in different fields, including:
- Material science: It helps researchers in understanding the magnetic behavior of new materials, which can lead to the development of advanced magnetic materials with tailored properties.
- Chemistry: The technique is employed to study the magnetic properties of chemical compounds, such as coordination complexes and organometallics, providing insights into their electronic structure and bonding characteristics.
- Geology: Gouy balance magnetometers are used to measure the magnetic susceptibility of rocks and minerals, which can provide valuable information about their formation and history, as well as aiding in the exploration of natural resources.
- Biomedical research: The study of magnetic properties of biological samples, such as cells and tissues, can help in understanding their structure, function, and response to external magnetic fields, with potential applications in diagnostics and therapy.
Conclusion
In summary, the Gouy balance magnetometer is a versatile and valuable tool for measuring the magnetic susceptibility of materials. Its wide applicability, accuracy, and non-destructive nature have made it an essential instrument in various fields of research and industry. Despite some limitations, the Gouy balance magnetometer continues to play a crucial role in the study of magnetism and the development of new magnetic materials.


